AWS Account Lifecycle

As your AWS footprint grows you will encounter the need to provision secure and compliant AWS Accounts in an automated way. Our Nuvibit Cloud Foundation Blueprint includes the Account Lifecycle, which addresses exactly this challenge. Our solution is not only able to provision new AWS Accounts, but also keeps them up to date and recycles them when they are no longer needed (a common requirement for experimental workloads).
We believe that GitOps is the best way for employees to order new resources. Therefore, a new AWS Account can be ordered with a simple pull request containing the required information.
|
|
Every AWS Account is defined in a dedicated config code block. Pull requests can be approved or denied after thorough review by the team responsible for your Cloud Foundation.
The Account Lifecycle determines the AWS Organizations Unit (OU) placement based on the defined attributes.
Naturally, the list of attributes can be extended to your organizational requirements (i.e. cost center, DNS zone, team name, manager mail).
The Account Lifecycle can also update these attributes later on and will automatically migrate AWS Accounts into the correct OU, initiate provisioning of network resources and for example assign a new owner.
All these attributes are stored as tags of the AWS Account and can be retrieved in your IaC definition.
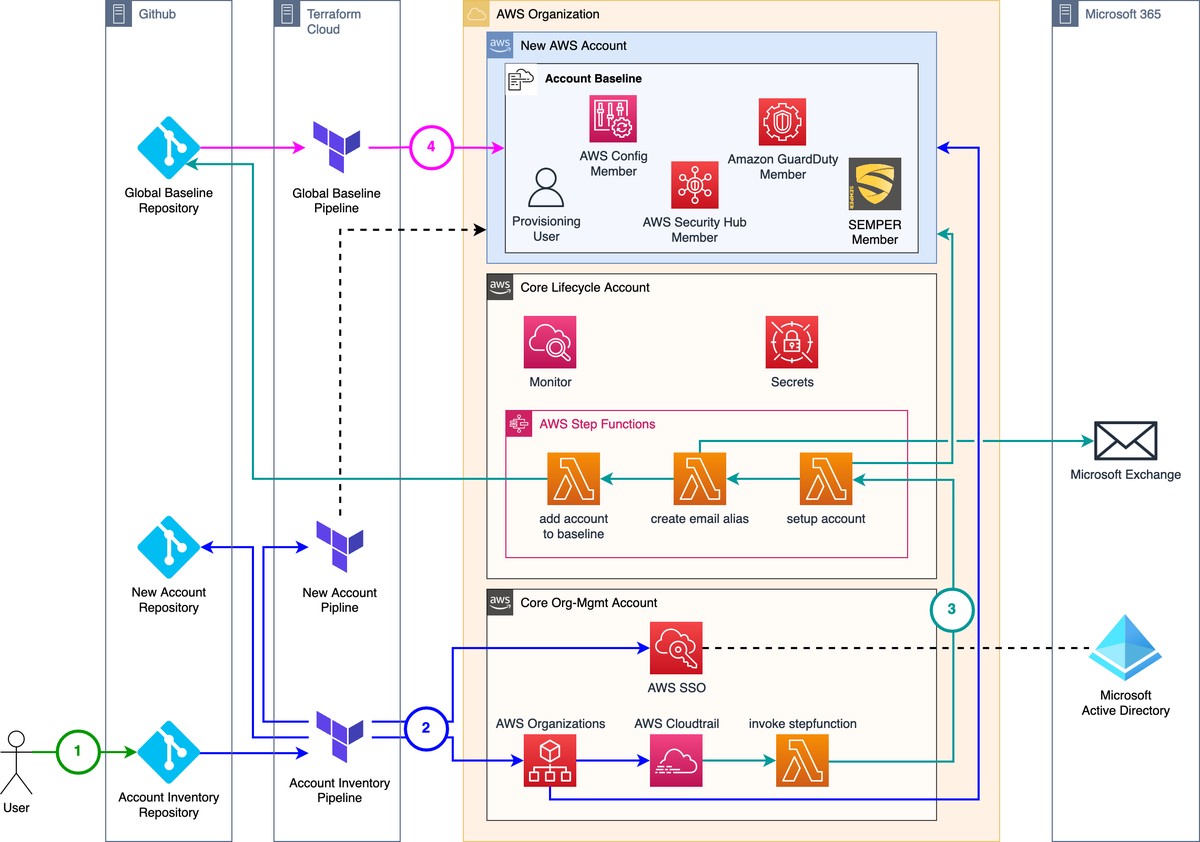
The rollout of a new AWS Account can be divided into four stages:
| Stage | Description |
|---|---|
| 1. Pull Request | The user creates a pull request in the account inventory repository containing all the required tags. The pull request is reviewed, approved and merged by the team responsible for the Cloud Foundation. |
| 2. Account Provisioning | Terraform is triggered by the merge commit and creates a new AWS Account, enables AWS SSO, creates a new repository and finally creates the CI/CD pipeline that provisions the workload resources to the AWS Account. In this example we use github for the code repositories and terraform cloud for CI/CD. |
| 3. Account Configuration | Not everything can be done via terraform as there are some tools and actions that are not yet supported. For those exceptions we implemented AWS Step Functions. The step functions are triggered by the CloudTrail Event that occurs as soon as a new account gets created. In our example we deploy three step functions: - setup account: deletes the default VPCs and all attached resources - create email alias: creates an email alias (in this example with Microsoft 365) - add account to baseline: Adds the new account to the global baseline repository |
| 4. Global Baseline | The commit to the global baseline repository triggers the pipeline of the global baseline. The account baseline is rolled out to the newly created account and all the core components of the foundation are updated to interact with the new account. To learn more about the global baseline and it’s components read our blog post about the Reference architecture for AWS Multi-Account Customers. |
AWS does not offer a simple solution to delete accounts in an automated manner. To bypass this constraint we implemented an account recycling feature. To recycle an AWS Account you can simply update the account inventory repository with the recycled flag:
|
|
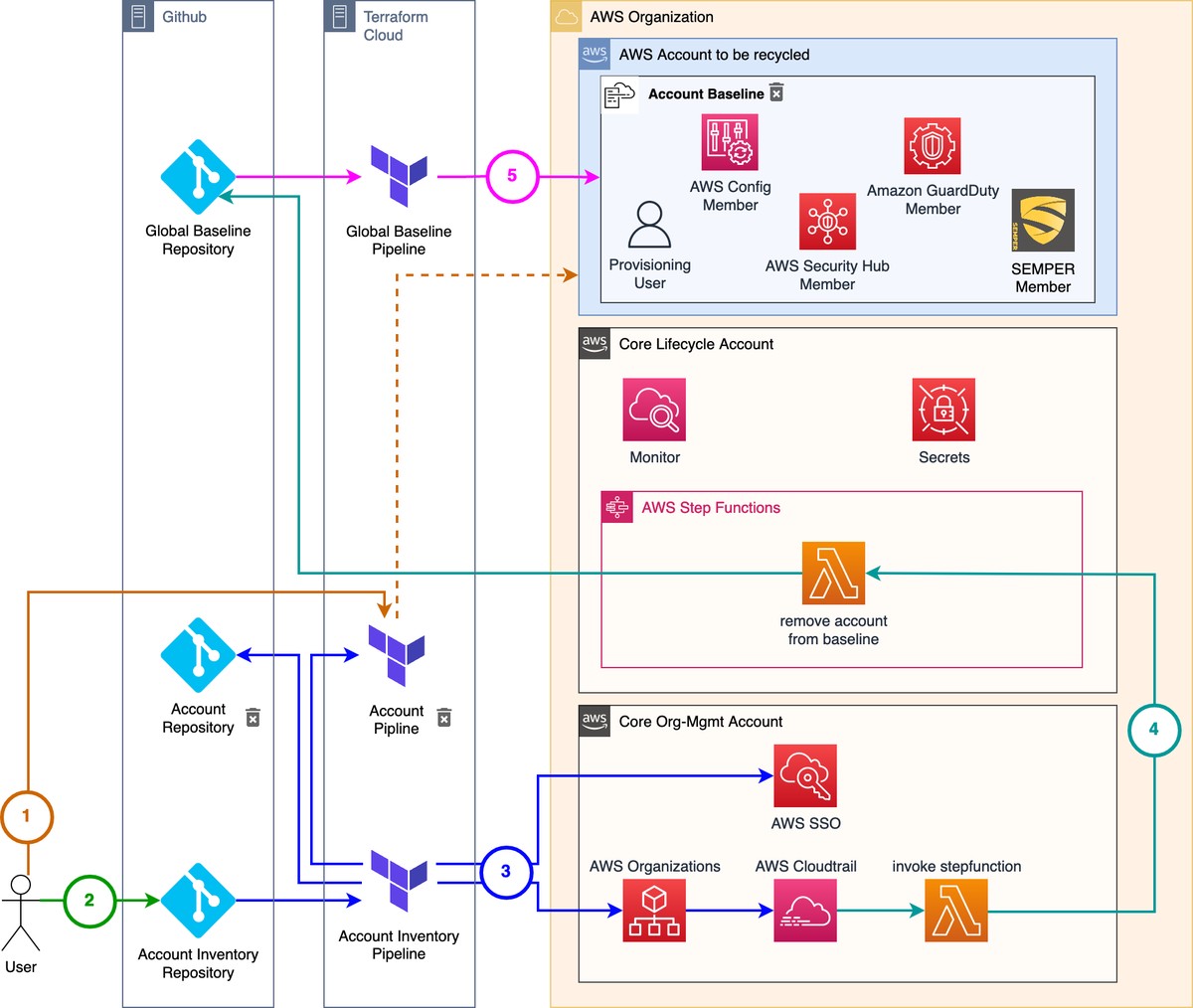
The recycling is done in five stages:
| Stage | Description |
|---|---|
| 1. Account Cleanup | The user has to perform a terraform destroy in his workspace to remove all resources that he has deployed over time. |
| 2. Pull Request | The user creates a pull request where he sets the recycled flag to true. |
| 3. Account recycling | Terraform removes the account pipline and repository and disables AWS SSO. Furthermore the account tags are updated to show that the account is recycled. |
| 4. Baseline Commit | The tag change creates a CloutTrail Event which in turn triggers the step function that removes the account from the global basline repository. |
| 5. Global Baseline | The commit to the global baseline repository triggers the pipeline of the global baseline. The account baseline is removed from the account and all the core components of the foundation are updated to prevent interaction with the new account. Again, to learn more about the global baseline and it’s components read our blog post about the Reference architecture for AWS Multi-Account Customers. |
The only thing left is an empty hull of the account that does not create any costs.
As soon as a new account is needed the recycled account can be reused by removing the recyled flag and updating the account attributes:
|
|
We understand that tooling is a very individual choice for every organization. It is crucial that the Account Lifecycle fits into the existing tooling landscape to reduce the learning curve for your teams as much as possible.
That is why we designed this solution to be highly flexible.
The CI/CD workflows can be implemented with the tooling of your choice (Jenkins, Bamboo, Gitlab, CircleCI, GitHub Actions, etc).
This solution will also work with any source control provider you may already have in place (GitHub, GitLab, Bitbucket, etc).
We highly recommend to use terraform for the deployment and management of your AWS Accounts and surrounding systems.
If you do not want to rely on Terraform Cloud or Terraform Enterprise, the workflows can also be implemented with the community edition of terraform and the CI/CD tooling of your choice.
Nuvibit specializes in providing Cloud Foundation Capabilities to organizations.
We will tailor our Foundation Blueprint to your needs and enable you to deliver Foundation Capabilities to your Cloud Workload Development Teams with a high level of maturity.
Get in touch with us for further details.